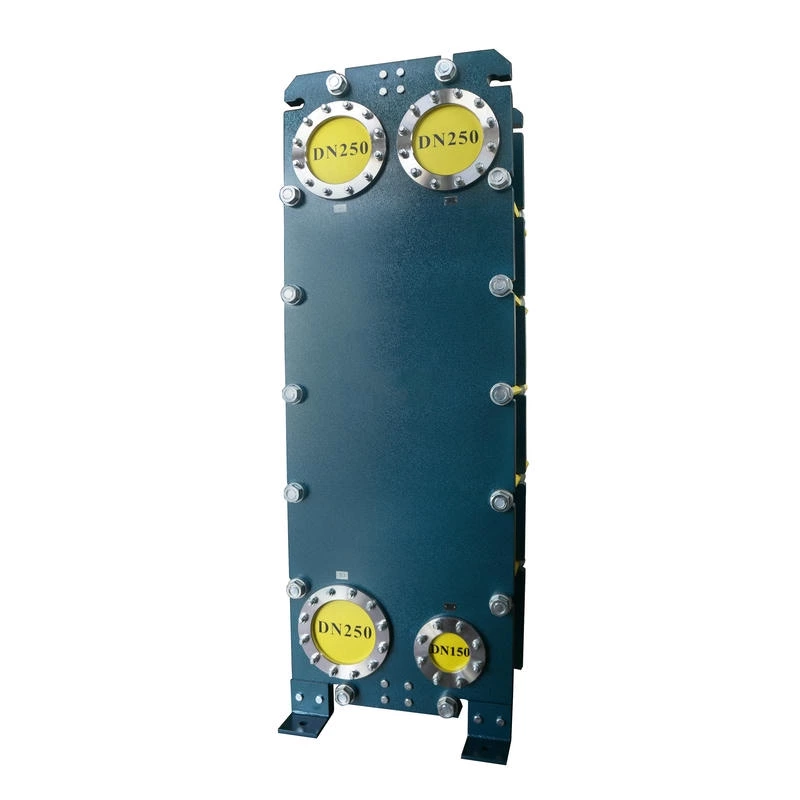
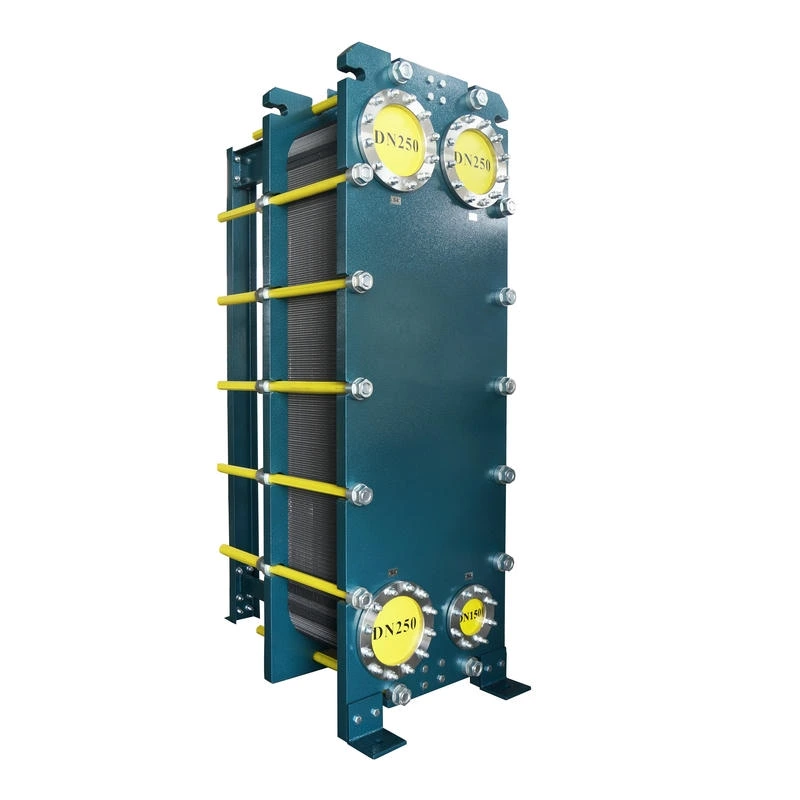
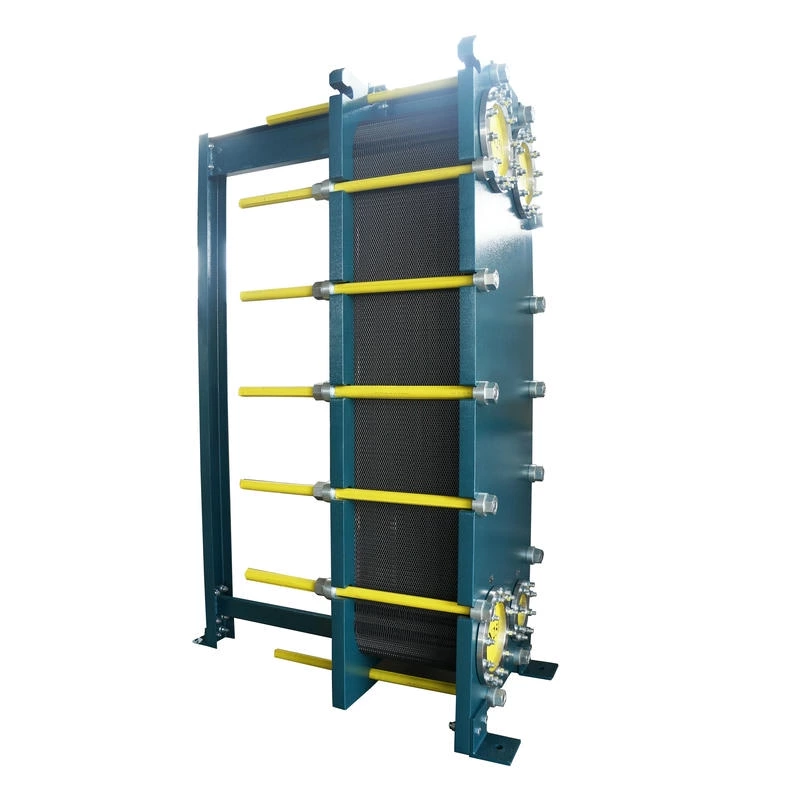
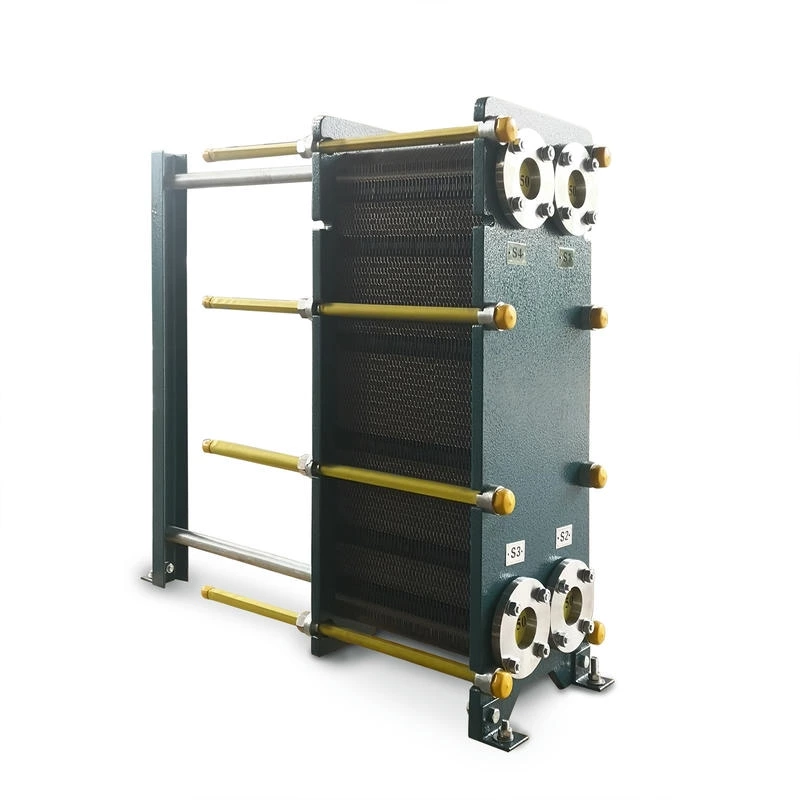
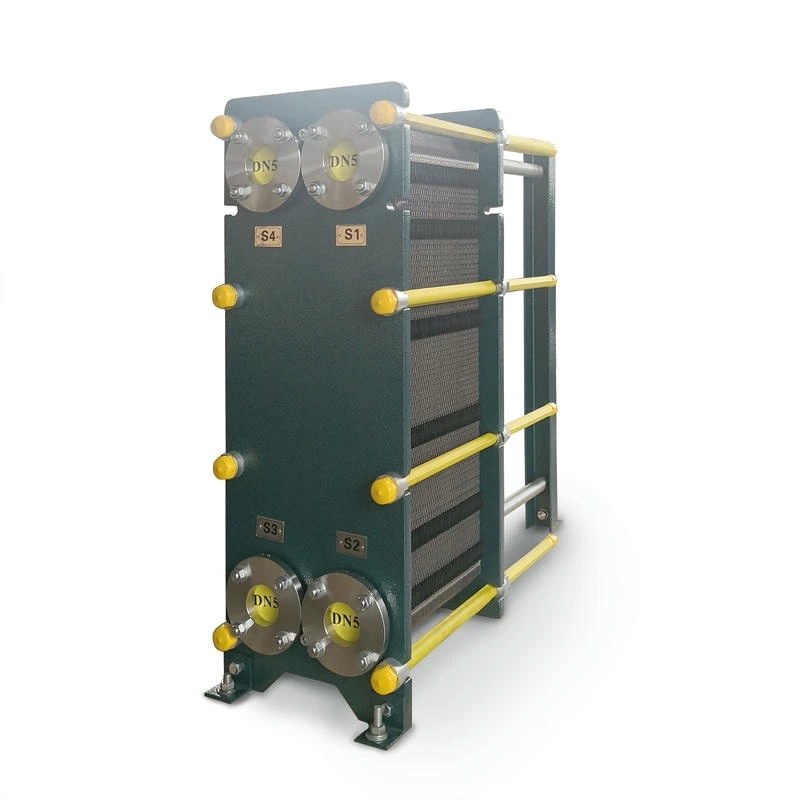
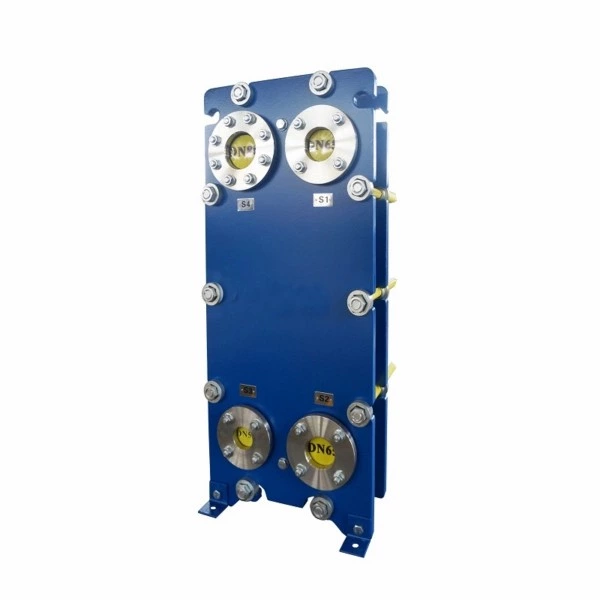
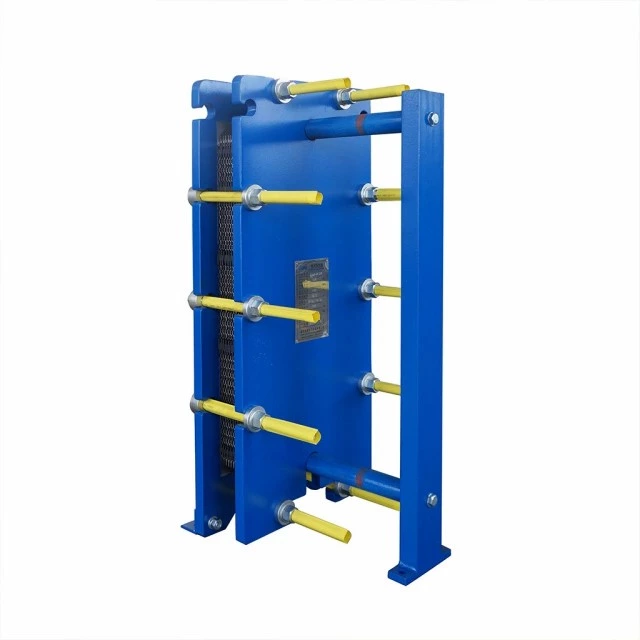
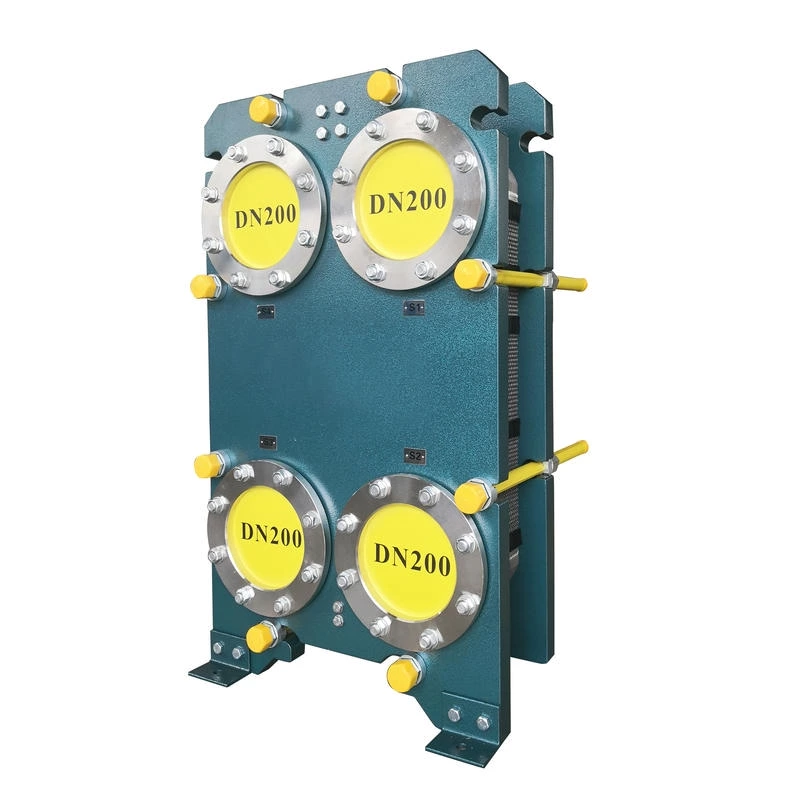
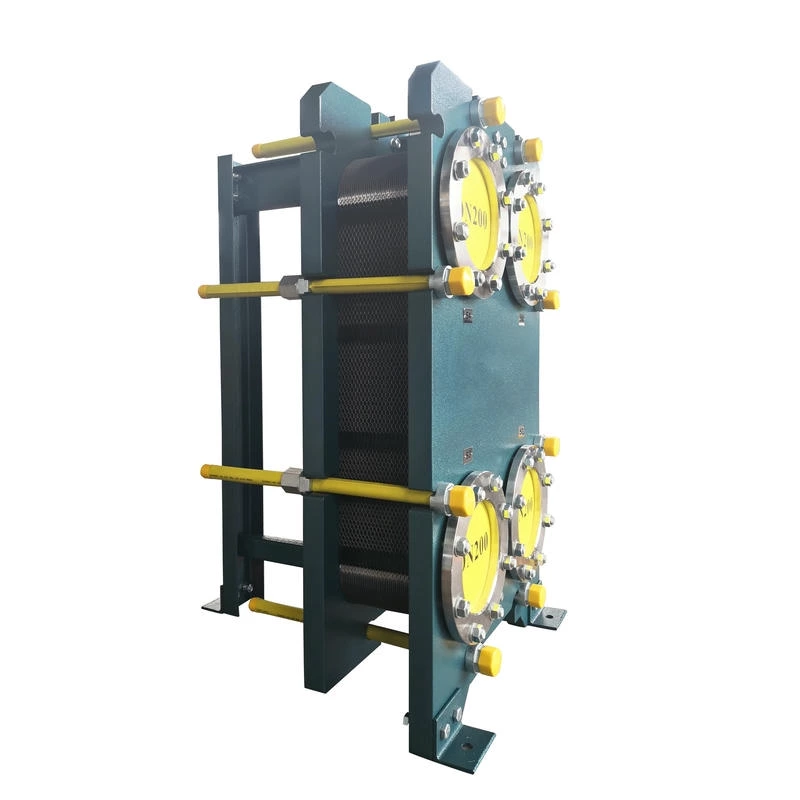
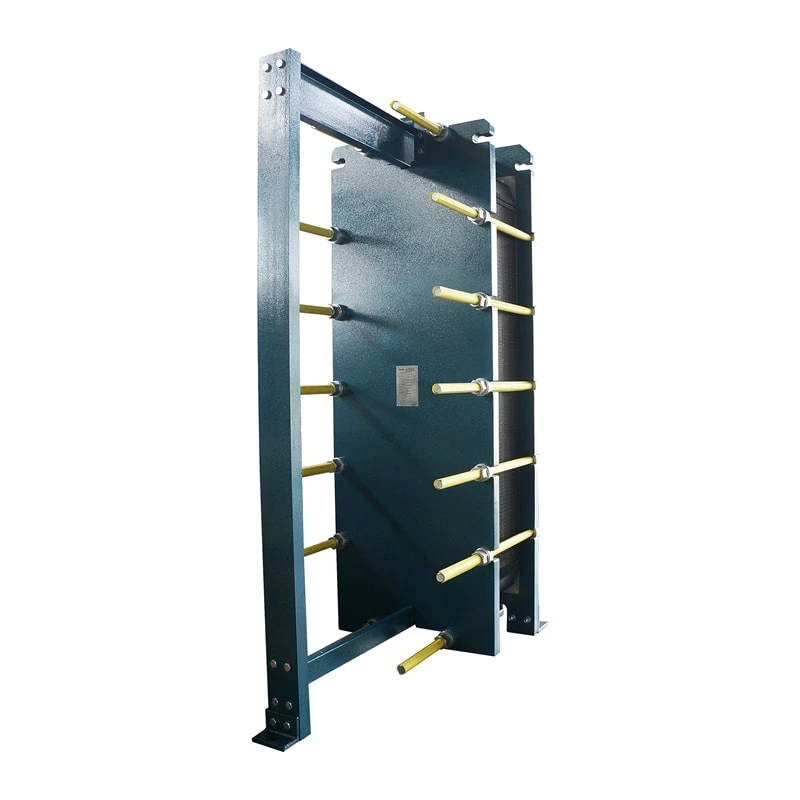
Wide channel plate heat exchanger BW250A
The wide-channel plate heat exchanger is specially optimized for handling media with high viscosity, containing particles or fibers, as well as fluids prone to scaling. The application limitations of ordinary plate heat exchangers under complex working conditions have been solved through a unique flow channel structure
Characteristics
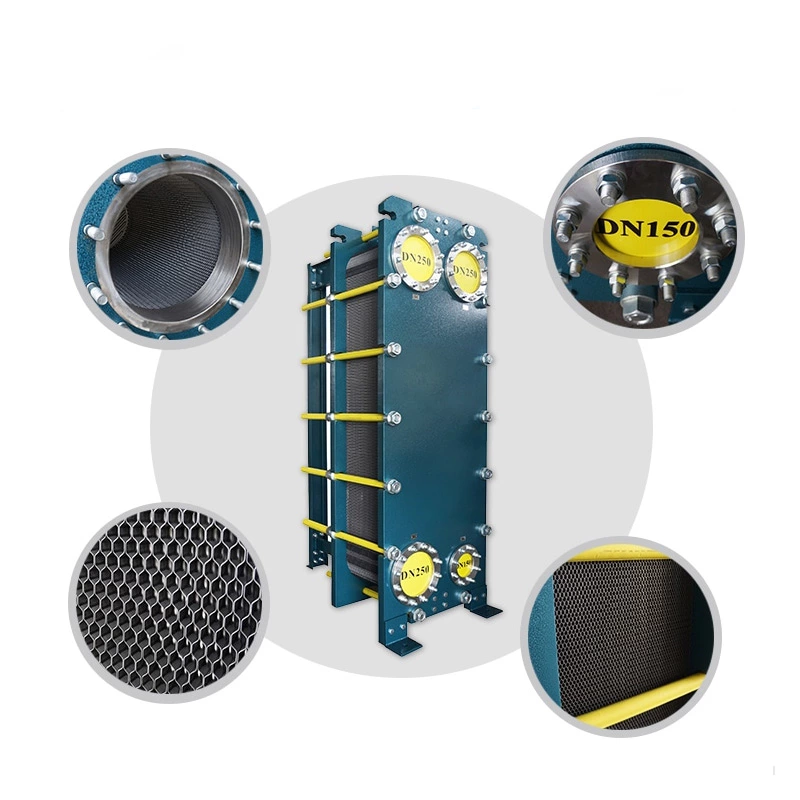
Wide-spaced flow channel design
The width of the flow channel can reach 2-5 times that of conventional plate heat exchangers, significantly reducing flow resistance and preventing particle or fiber accumulation and blockage. It is suitable for slurries, sludges, syrups, etc., which are high-viscosity or contain impurities.
Enhanced heat transfer technology
Special stamping processes (such as inclined waves, spherical protrusions, etc.) are adopted for corrugated plates, ensuring turbulent flow even when the flow channel is widened. The heat transfer coefficient can reach 3-5 times that of shell-and-tube heat exchangers.
Anti-scaling and easy maintenance
The large flow channel reduces stagnant areas, combined with the detachable plate structure, facilitating mechanical cleaning or chemical cleaning, significantly extending maintenance cycles and reducing downtime costs.
Material and seal compatibility
Available in stainless steel, titanium, Hastelloy, etc. The sealing gasket has a wide temperature range (-40℃ to 200℃), suitable for corrosive media or high-temperature conditions.