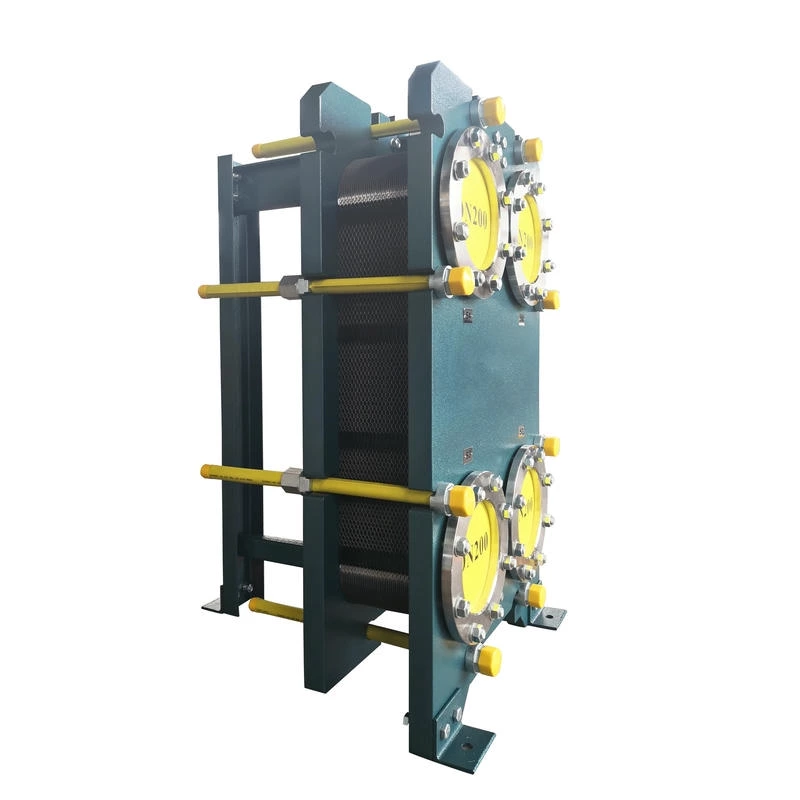
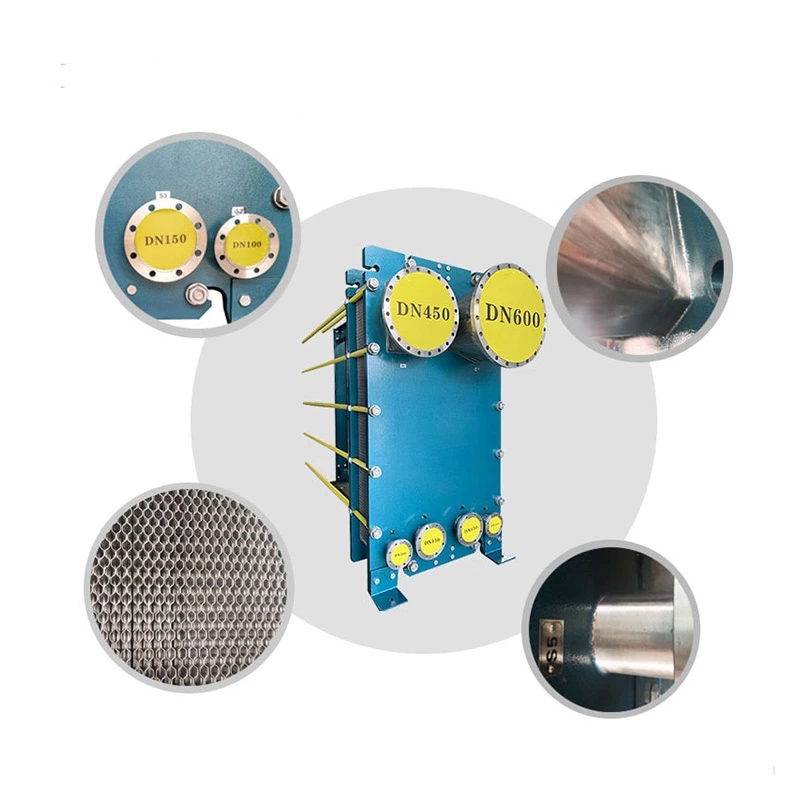
Plate Evaporator S600
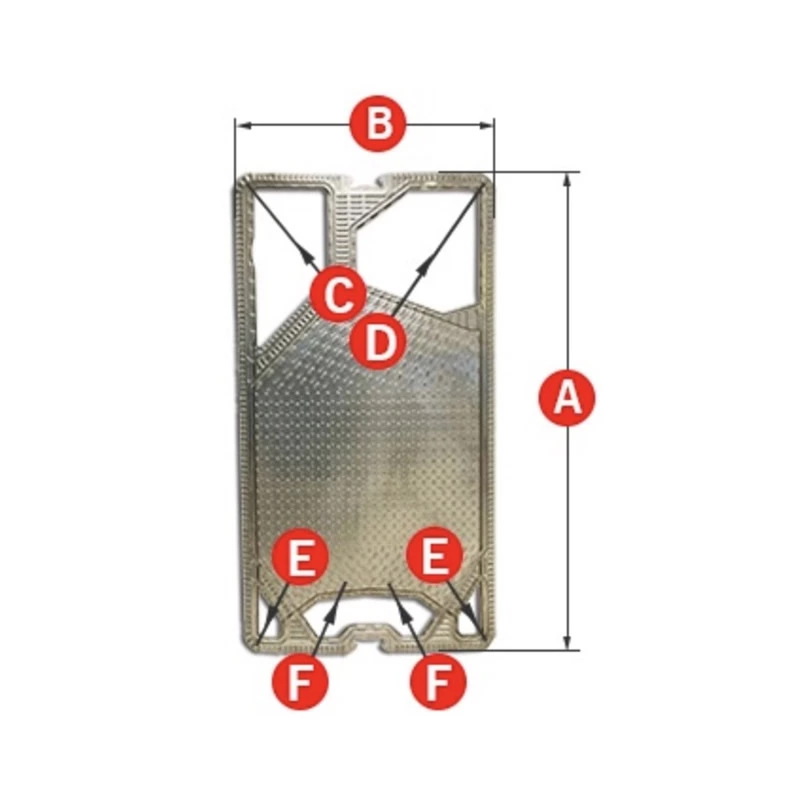
Plate evaporator uses corrugated plates as heat transfer elements, and heat exchange is carried out through the flow channels between plates to realize evaporation and concentration of feed liquid.
Characteristics
- Efficient heat transfer: The turbulent design enables a heat transfer coefficient as high as 3000-6000 W/(m²·K), which is 3-5 times that of tubular evaporators.
- Compact and energy-saving: Small in size and large in heat exchange area, it can save 30-50% of energy consumption.
- Flexible and adjustable: The processing capacity can be adjusted by increasing or decreasing the number of plates to meet different production demands
- Suitable for heat-sensitive materials: Short residence time (only a few seconds), reducing the damage to heat-sensitive components.
- Easy to maintain: Detachable and washable, suitable for high-viscosity or easily scaling materials.
Limitations:
It is not suitable for materials with high viscosity (>500cp) or containing solid particles.
The sealing gasket may age after long-term use and needs to be replaced regularly.